臭氧作为一种重要的温室气体和大气氧化剂,是气候变化及生态环境研究重点关注的大气成分之一。其中平流层臭氧占大气臭氧总量约90 %,它的存在及浓度的变化会对人类的生存环境和全球气候的变化产生极其重要的影响。近几年来,平流层臭氧异常对对流层天气气候的影响是国际上的前沿研究热点之一。以往的研究已发现南极平流层臭氧损耗对南半球对流层天气气候有重要影响,但是,北极平流层臭氧是否对北半球哈德莱环流边界和副热带降水产生影响及影响机理并不清楚。近期,我院胡定珠老师、管兆勇教授等针对此问题展开研究取得新进展,相关成果发表于Geophysical Research Letters.
研究发现,北半球春季Hadley环流北边界和北极平流层臭氧在1979-2014年间年际时间尺度上存在反相关系。北极平流层臭氧每降低一个标准偏差对应Hadley环流北边界向极地移动0.67°,而北极平流层臭氧每增加一个标准偏差对应Hadley环流北边界向赤道移动?0.45°。多套资料分析和数值模拟结果都表明,北极平流层臭氧增加主要通过减弱涡动动量通量导致Hadley环流北边界及副热带雨带向赤道移动,并伴随副热带静力稳定性的减少,副热带的负涡动量通量散度异常和经向北风异常。此项研究结果有助于深入了解中高纬度相互作用,尤其对副热带降水和水循环的研究有重要意义。
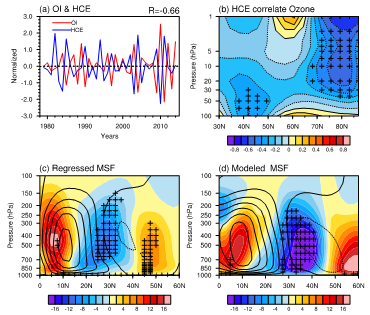
Figure 1. (a) Normalized time series of the HCE (blue) and OI (red) in MAM during 1979–2014. The value on the top-right corner is the correlation coefficient between HCE with OI. (b) Correlations between the HCE and zonal-mean ozone. (c) Anomalies in the MSF (shading, 109 kg s–1) regressed on the OI during boreal spring over 1979–2014. Superimposed solid and dashed contours indicate the positive and negative MAM mean of MSF, respectively. (d) Same as (c), but for the WACCM simulated differences in the MSF (shading, 108 kg s–1) and the superimposed solid and dashed contours are for the positive and negative MAM mean of MSF in control run, respectively, and the contour interval is 2×1010 kg s–1. The areas with crosses are values significant at/above the 95% confidence level.
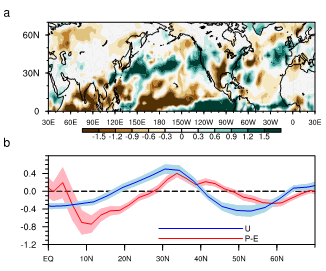
Figure 2. (a) Regressed anomalies in the differences between the precipitation and evaporation (P–E) on the OI in boreal spring during 1979–2014. (b) Zonal-mean P–E (red lines; mm day–1) with 0.5 standard deviation (red shading), and 200 hPa zonal winds from MERRA (blue lines; 5 m s–1) with 0.5 standard deviation (blue shading) regressed on the OI.
参考文献:
Hu, D., Z. Guan, W. Tian, 2019: Signatures of the Arctic stratospheric ozone in the Northern Hadley circulation extent and subtropical precipitation. Geophys. Res. Lett., 46, 12,340-12,349.