厄尔尼诺(El Nino)是发生在热带太平洋最显著的气候异常信号,它与我国夏季降水异常之间存在着复杂的联系。研究不同型厄尔尼诺在发展阶段对东亚夏季降水的影响及物理机理,对提高我国夏季降水预报能力、减少预测不确定性有重要意义。
大气科学学院温娜副教授团队的研究结果表明:在发展阶段,不同型El Nino对我国夏季降水异常的影响存在显著差别。对东部型(EP)El Nino,降水异常呈偶级型分布,华北降水异常偏少,而华南沿海降水异常偏多;对混合型(MP)El Nino,江淮流域降水异常偏多,而华南降水异常偏少;对中部型(CP)El Nino,降水异常呈三级型分布,华北和华南降水异常偏多,而江淮地区降水异常却异常偏少。这三型厄尔尼诺对东亚夏季降水及环流的不同影响主要是由于赤道中东太平洋不同型El Nino海温异常引起的Walker环流尺度不同,从而造成赤道外高层大气辐合辐散场的差异,最终急流扰动位置的不同导致大气响应的差别。

Figure 1 Different types of summer El Niño (a, c, e) and corresponding summer precipitation anomalies over East Asia (b, d, f). a) Summer eastern Pacific (EP) El Niño, cases selected on the base of the maximum SST anomaly (at least greater than 0.5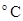 ) falling into the region (
) falling into the region ( ,
,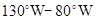 ) (as indicated by the blue box) during the summer preceding the peaks of El Niño. c) Summer mixed-type Pacific (MP) El Niño, based on the maximum SST anomaly over the region (
) (as indicated by the blue box) during the summer preceding the peaks of El Niño. c) Summer mixed-type Pacific (MP) El Niño, based on the maximum SST anomaly over the region ( ,
, ). e) Summer central Pacific (CP) El Niño, based on the maximum SST anomaly over the region (
). e) Summer central Pacific (CP) El Niño, based on the maximum SST anomaly over the region ( ,
, ). Panels. b, d and f are composite precipitation anomalies in summer over East Asia, corresponding to summer EP, MP and CP El Niño respectively. In the upper panels, the red (blue) shading with the white solid (dashed) line represents positive (negative) values with contour interval (CI) of 0.3
). Panels. b, d and f are composite precipitation anomalies in summer over East Asia, corresponding to summer EP, MP and CP El Niño respectively. In the upper panels, the red (blue) shading with the white solid (dashed) line represents positive (negative) values with contour interval (CI) of 0.3 . In the botttom panels, blue (red) shadings with the white solid (dashed) lines denote positive (negative) percentage anomalies relative to climatology with CI=5%. The thick black contour indicates the 90% confidence level.
. In the botttom panels, blue (red) shadings with the white solid (dashed) lines denote positive (negative) percentage anomalies relative to climatology with CI=5%. The thick black contour indicates the 90% confidence level.

Figure 2 Composite Walker Circulation anomalies over the equator ( ) (unit:
) (unit: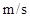 ), in association with the different types of summer El Niño. The vertical velocities are magnified by 100 times. The upper, middle and bottom panels correspond to summer EP, MP and CP El Niño, respectively. The red/blue shadings indicate the 90% confidence level for air ascending and descending.
), in association with the different types of summer El Niño. The vertical velocities are magnified by 100 times. The upper, middle and bottom panels correspond to summer EP, MP and CP El Niño, respectively. The red/blue shadings indicate the 90% confidence level for air ascending and descending.
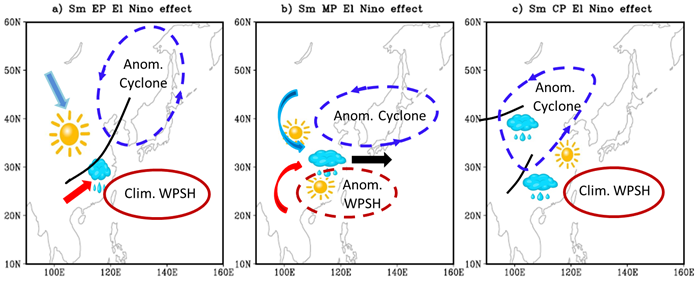
Figure 8 Schematic diagrams showing the impact of different types of El Niño in developing summer on East Asian summer precipitation. a) For summer EP El Niño, the dipole precipitation response with anomalous wetness in Southeast China and anomalous dryness in northern China is mainly due to the El Niño-induced low pressure anomaly over Northeast Asia, as indicated by the blue dashed circle. The dark red solid circle indicates the climatological mean of the West Pacific Subtropical High. b) For summer MP El Niño, the typical tripole precipitation anomaly with wet conditions along the Yangtze-Huaihe River valley and dry conditions in South and North China and is mainly due to the confrontational situation of the El Niño-induced low pressure anomaly over Northeast Asia (the blue dash circle) and the westward shift of the Western Pacific Subtropical High (the dark red dashed circle). c) For summer CP El Niño, the triangle-pattern precipitation anomaly with anomalous wetness in northern and southern China and anomalous dryness in the Jianghuai Region is mainly attributed to the abnormal cyclone occupying central-north East Asia (the blue dashed circle). The dark red solid circle indicates the climatological mean of the Western Pacific Subtropical High. The vectors in the sketch denote the wind direction with red and blue indicating warm and cold air respectively.
文章信息:
Wen, N., Li,Laurent & Luo, JJ. 2020, Direct Impacts of Different types of El Nino in Developing Summer on East Asian Precipitation, Clim Dyn. 55, 1087–1104