大气边界层高度是表述边界层结构的关键变量之一,在垂直湍流混合、大气边界层对流运动和陆-气耦合中起决定性作用。而土壤湿度作为陆面过程中的重要参量,与地表能量平衡密切相关,它可以改变地表反照率、土壤热容量、感热及潜热通量,从而直接或间接影响边界层的演变。近日,我院陆气相互作用团队的陈海山教授及其博士生许智棋和中国气象科学研究院大气成分所郭建平研究员团队合作,通过观测分析探讨了不同热力状态下土壤湿度对日间边界层高度的作用及其区域性差异,相关成果发表于《Geophysical Research Letters》。
研究发现:日间对流与中性边界层高度和土壤湿度之间普遍存在较强的负相关,这与土壤湿度和感热通量之间的负相关关系有关,其空间型呈“西北弱 东南强”,区域性差异较大;相反,日间稳定边界层高度与土壤湿度呈显著的正相关。这是因为当边界层处于稳定状态时,间歇性干扰取代了感热通量,成为调节边界层演变的主导因素,而较高的土壤湿度会引起较多水汽和流体的间歇性扰动。边界层高度对土壤湿度的依赖性存在区域性差异,日间对流与中性边界层高度在干区与气象要素关系更密切,在湿区与土壤湿度关系更密切。这可能是由于干旱区,尤其是西北地区,对流层低层非常干燥,在这种情况下,促进边界层发展的对流发生完全由大气条件决定,多云、潮湿、稳定的大气导致对流与中性边界层高度变浅。在干区,感热通量和边界层高度之间的相关性强于湿区(干区对流边界层:0.25, 中性边界层:0.33;湿区对流边界层:0.16,中性边界层:0.18)。湿区较高的潜热通量会通过复杂的物理过程抑制边界层的发展。
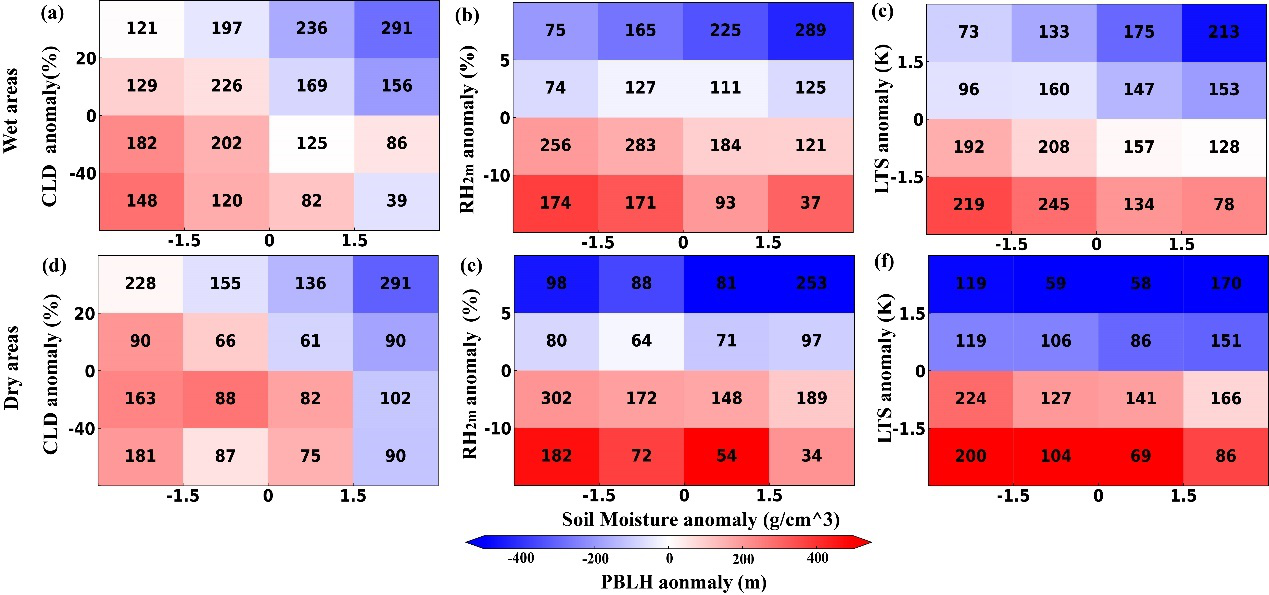
Figure 1. Joint dependence of the SM anomalies on PBLH anomalies over wet (a, b, c) and dry (d, e, f) areas for CBL versus the anomalies of CLD (a, d), RH2m (b, e), and LTS (c, f). The bold number in each cell indicated the number of samples in the cell. The color bar denotes the normalized PBLH averaged in each cell. RH2m, as a convoluted parameter (temp, pressure, humidity), can indicate the low-level humidity to some extent considering the absence of humidity measurements. For a given site, the monthly mean during the period 2012–2016 was removed from daily values for the above-mentioned parameters to avoid the effect of seasonal, spatial, and long-term variation.
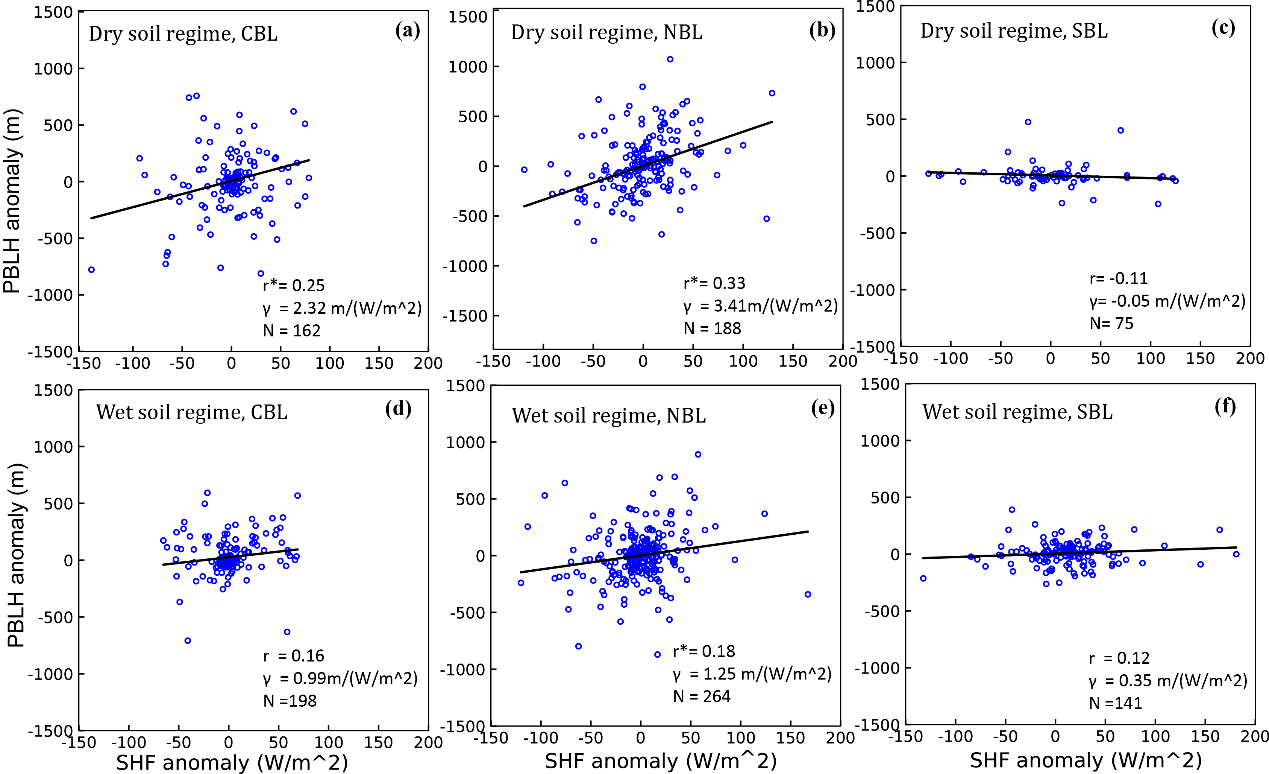
Figure 2. Scatter plots and linear regression analyses between monthly-mean PBLH and SHF anomalies over dry (a, b, c) and wet (d, e, f) area as constraint for CBL (a, d), NBL (b, e), and SBL (c, f) regimes at 1400 BJT, respectively. Also shown are the correlation coefficient r and gradient γ (in m/w/m^2) values. Gradient γ donates the change of PBLH with changing SHF. r with asterisks indicates statistically significant trends at a 99% confidence level. The blue dot denotes the anomalies for a given site, where the monthly mean during the period 2012–2016 was removed from daily values for the above-mentioned parameters to avoid the effect of seasonal, spatial, and long-term variation.
相关文献:
Xu Z., H. Chen*, J. Guo*, W. Zhang. Contrasting effect of soil moisture on the daytime boundary layer under different thermodynamic conditions in summer over China[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2021, 48(3): e2020GL090989.