在全球变暖的大背景下高温热浪事件呈现增多、增强的趋势,对自然系统和人类社会造成重要影响。区域高温热浪的变化及风险预估对于气候变化适应和灾害风险管理具有重要意义。周波涛教授团队基于区域气候模式(RegCM4)动力降尺度模拟对RCP4.5情景下中国区域未来高温热浪的频次及强度变化进行了精细化预估。
研究结果表明,和当前气候(1986–2005)相比,中国区域未来高温热浪的频次和强度均明显增加。其中,增长的持续时间是高温热浪强度增加的主要因素。
除此之外,高温热浪的发生风险预估在未来进一步增加:21世纪末期(2080–2099),西南和华南地区极端热浪(强度超过参考期99%分位数的事件)的发生风险分别是当前气候状况下的64倍和53倍;破纪录(超过当前气候下的最大值)的高温热浪频次几乎每年都会出现,破纪录的热浪强度也会在华南、华中和华东地区每1–2年出现一次。本研究加深了对未来中国区域高温热浪变化的理解,并为气候变化的适应和减缓提供了更多精细化的信息。
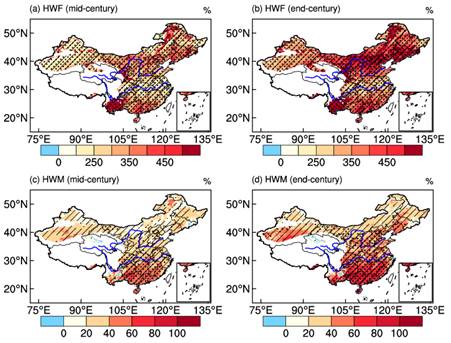
Figure1:MME projected percentage changes in (a, b) HWF and (c, d) HWM in the mid-century (left-hand panels) and the end-century (right-hand panels) relative to 1986–2005. Dots indicate the regions where the changes are above the 0.05 significance level and the hatching indicates the regions where all the ensemble members agree on the sign of change.
相关论文信息:
Xie Wenxin, Zhou Botao, Han Zhenyu, Xu Ying. Projected changes in heat waves over China: Ensemble result from RegCM4 downscaling simulations. International Journal of Climatology, 2021, 41, 3865–3880. doi:10.1002/joc.7047.
Xie Wenxin, Zhou Botao, You Qinglong, Zhang Yuqing, Ullah Safi. Observed changes in heat waves with different severities in China during 1961-2015. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 2020, 141: 1529-1540. doi:10.1007/s00704-020-03285-2